Application Of Dry Process Technology In The Manufacturing Of Automobiles And Related Products
Application Areas
Automobile Headliners: The dry process plays a crucial role in manufacturing automobile headliners. These are the interior ceiling coverings of vehicles. A well - made headliner not only provides an aesthetically pleasing interior but also contributes to sound insulation and heat resistance. The dry process enables the creation of headliners with precise shapes and high - quality finishes that can withstand the vibrations and environmental conditions within a vehicle.
Carpets: Automotive carpets are another key application area. Carpets need to be durable, resistant to stains, and able to conform to the irregular floor shapes of vehicles. The dry process allows for the production of carpets with excellent texture and dimensional stability, ensuring a perfect fit in the car's interior.
Coat Racks: Coat racks in vehicles, often located in the rear or side compartments, require materials and manufacturing processes that can support the weight of hanging items and withstand daily use. The dry process helps in creating coat racks with sufficient strength and a smooth surface finish.
Front Walls: The front walls of a vehicle, which are part of the interior structure, need to be strong and well - finished. The dry process is employed to produce front walls that can meet the safety and aesthetic requirements of modern automobiles.
Production Process Details
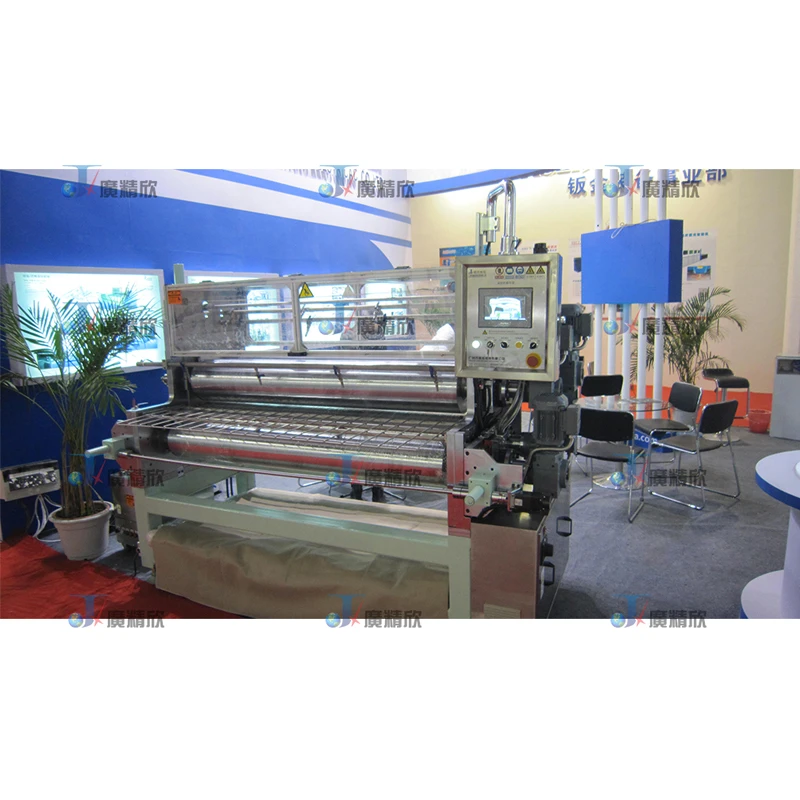
Heat Sources in the Dry Process
Hot Air Circulation: In this method, hot air is circulated around the materials to be processed. Specialized ovens or heating chambers are used. The hot air uniformly heats the materials, such as the base materials for headliners or carpets. This even heating ensures that the materials reach the desired temperature for subsequent processing steps. The circulation system is designed to maintain a consistent temperature throughout the chamber, minimizing temperature gradients and ensuring uniform treatment of the products.
Infrared Ceramics: Infrared ceramic heaters are used to emit infrared radiation. When these heaters are directed at the materials, the infrared rays are absorbed by the surface of the materials. This absorption causes the molecules within the materials to vibrate, generating heat. This method is highly efficient as it can quickly heat the surface of the materials without heating the surrounding air as much as hot air circulation. It is especially useful for materials that require rapid and precise heating, like some synthetic fabrics used in headliners.
Oil Heating Plate: Oil heating plates are another source of heat in the dry process. These plates are filled with heat - conducting oil. When an electrical heating element heats the oil, the heat is transferred to the surface of the plate. The materials to be processed are placed in contact with the heated plate. The oil heating plate provides a stable and uniform heat source, which is beneficial for processes that require a specific and constant temperature, such as the shaping of certain plastic components in coat racks.
Light Wave Heating: Light wave heating, also known as radiant heating, uses high - intensity light sources. These light waves are absorbed by the materials, converting light energy into heat energy. This heating method can be very fast and is often used when quick heating is required, for example, in the pre - heating stage of forming front wall components.
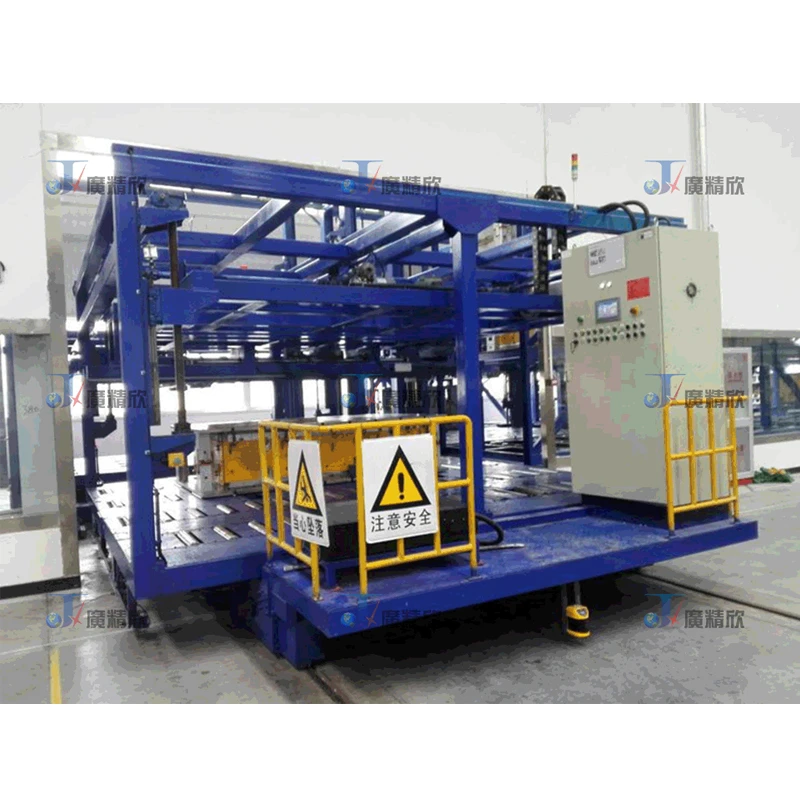
Cold Molding
After the materials have been heated using one of the above - mentioned methods, they are then subjected to cold molding. Cold molding involves placing the heated materials into a mold at room temperature or a relatively low temperature. The shape of the mold determines the final shape of the product. As the heated materials cool down in the mold, they solidify and take on the shape of the mold. This process helps in achieving precise shapes and dimensional accuracy. The cold mold also helps in setting the structure of the materials, enhancing their mechanical properties.
Advantages of the Dry Process
Energy Efficiency: Compared to some wet - based processes, the dry process can be more energy - efficient. For example, infrared ceramic and light wave heating methods directly transfer energy to the materials, reducing heat loss to the surrounding environment. Hot air circulation systems can also be optimized to recycle and reuse heat, minimizing energy consumption.
Clean and Environmentally Friendly: Since the dry process does not involve the use of liquid substances like adhesives in large quantities (unlike wet processes), it produces less waste and is generally more environmentally friendly. There is no need to deal with the disposal of liquid waste or the drying of wet - coated materials, which simplifies the production process and reduces the environmental impact.
Versatility: The dry process can be applied to a wide range of materials, including various synthetic fabrics, plastics, and composite materials. This versatility allows manufacturers to choose the most suitable materials for different automotive components based on performance requirements, cost, and aesthetic considerations.
In conclusion, the dry process, with its diverse heat sources and cold - molding technique, offers a reliable and efficient solution for the production of automotive headliners, carpets, coat racks, front walls, and other related products. It continues to play an important role in meeting the high - quality and high - volume production demands of the automotive industry.
- Automotive Headliner Wet Production Line
- Automotive Headliner Dry Production Line
- Automotive Fabric Lamination Line
- Carpet Production Line
- Wheel House & Interior Sound Insulation Pad Production Line
- Interior Cutting Equipment
- Automobile Headliner Assembly Line
- Interior Form And Die
- Production Auxiliary Equipment
- Home
- Products
- Automotive Headliner Wet Production Line
- Automotive Headliner Dry Production Line
- Automotive Fabric Lamination Line
- Carpet Production Line
- Wheel House & Interior Sound Insulation Pad Production Line
- Interior Cutting Equipment
- Automobile Headliner Assembly Line
- Interior Form And Die
- Production Auxiliary Equipment
- Application
- About Us
- Resources
- News
- Contact
- featuredproducts